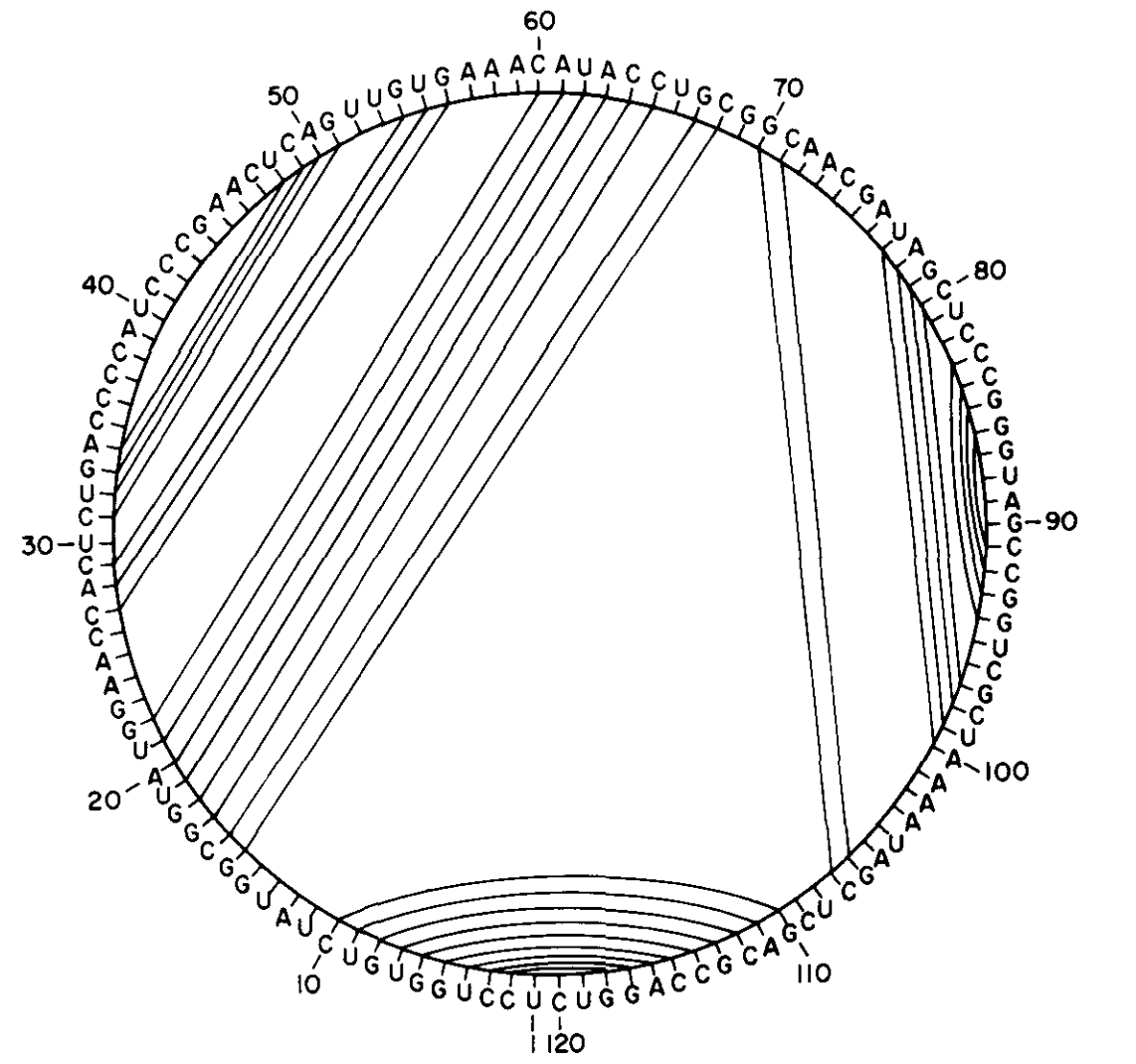
The simplest way of representing secondary structure is through a curved line connecting a series of equidistant points on a circumference on a circle. Due to the knot and pseudo-knot condition, no curved lines should overlap, and no point should be part in more than one curved line. This type of representation was introduced by Nussinov et al.
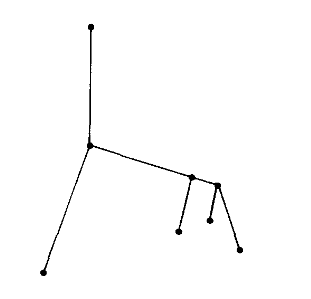
A more abstract type of representation is as a tree (or a forest of trees, borrowing a term from mathematical graph theory.